Molecular dynamics simulation of the spherical electrical double layer of a soft nanoparticle. Effect of the surface and counterion valence.
Molecular dynamics simulation of the spherical electrical double layer of a soft nanoparticle. Effect of the surface and counterion valence
M. Nedyalkova, S. Madurga, S. Pisov, I. Pastor, E. Vilaseca, F. Mas.
J. Chem. Phys., 137 (2012) 174701.
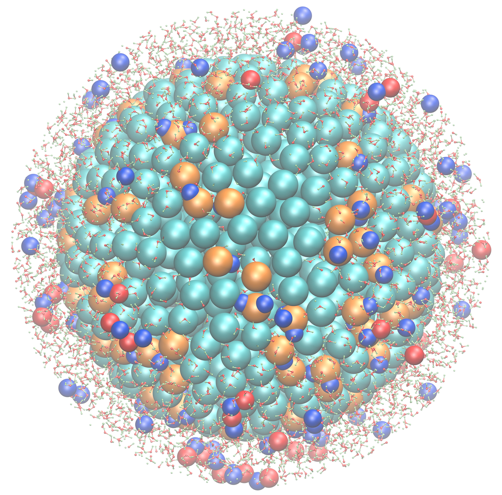
Snapshot of a simulation of the −100e charged nanoparticle in 1 M NaCl solution.
Only water molecules, Na+ ions (in blue), and Cl− ions (in red) close to 1.0 nm from the nanoparticle surface are displayed.
Molecular dynamics simulations were performed to study the ion and water distribution around a spherical charged nanoparticle. A soft nanoparticle model was designed using a set of hydrophobic interaction sites distributed in six concentric spherical layers. In order to simulate the effect of charged functionalyzed groups on the nanoparticle surface, a set of charged sites were distributed in the outer layer. Four charged nanoparticle models were studied in NaCl and CaCl2 salt solutions at 1 M and 0.1 M concentrations to evaluate the effect of the surface charge, counterion valence, and concentration of added salt. We obtain that Na+ and Ca2+ ions enter inside the soft nanoparticle. Monovalent ions are more accumulated inside the nanoparticle surface.
