A New type of Strong Metal-Support Interaction and the Production of H2 through the Transformation of Water on Pt/CeO2(111) and Pt/CeOx/TiO2(110) catalysts.
A New type of Strong Metal-Support Interaction and the Production of H2 through the Transformation of Water on Pt/CeO2(111) and Pt/CeOx/TiO2(110) catalysts
A. Bruix, J. A. Rodriguez, P. J. Ramírez, S. D. Senanayake, J. Evans, J. B. Park, D. Stacchiola, P. Liu, J. Hrbek, F. Illas
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 134 (2012) 8968.
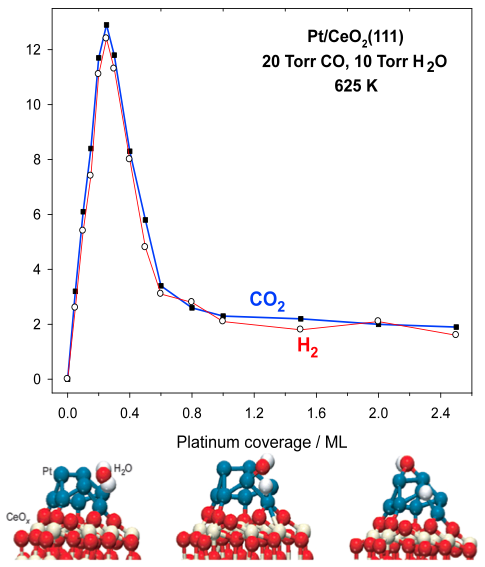
Experimental values of hydrogen production through the water gas shift (WGS) reaction catalyzed by Pt
nanoparticles supported on CeO2 as a function of the particle size in the Pt/CeO2 catalys and model used to explain the observed phenomenon
The WGS reaction, CO + H2O ® CO2 + H2, is used in industry to remove the CO produced in hydrocarbon steam reforming which is the main source of molecular hydrogen. The small amount of CO left in the gas stream poisons the catalysts used in subsequent processes such as hydrotreatment to remove S from oil in the refineries before entering cracking or in the fuell cells. In this work, experiments show that the reactivity of Pt nanoparticles supported on CeO2 changes dramatically with particles size. The theoretical models and computational work carried out by IQTCUB researchers show that the origin of this behavior is a new specific support effect which, in this way, participates directly in the chemical reaction. This effect has been highlighted by Prof. C. T. Campbell in a note recently published in Nature Chemistry 4 (2012).
