Benzene-Hydrogen Bond (C6H6-HX) Interactions: The Influence of the X Nature on their Strength and Anisotropy
Benzene-Hydrogen Bond (C6H6-HX) Interactions: The Influence of the X Nature on their Strength and Anisotropy
M. Albertí, A. Aguilar, F. Huarte-Larrañaga, J.M. Lucas, F. Pirani
J. Phys. Chem. A, 118 (2014) 1651
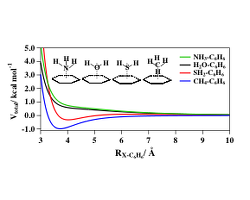
H2O-C6H6, SH2-C6H6, NH3-C6H6, and CH4-C6H6
intermolecular interaction potentials for the represented molecular approaches
The intermolecular potential energy of the C6H6-SH2 and C6H6−NH3 dimers is formulated as combination of electrostatic and nonelectrostatic contributions. The relevant parameters, derived from molecular polarizability components, allow describing in a consistent way both size repulsion and dispersion attraction forces. The features of the most stable configurations predicted by the potential model have been compared with available ab initio and experimental data. Moreover, the strength of the C6H6−HX interaction has been analyzed by comparing the obtained results with the corresponding ones for the C6H6−H2O and the C6H6−CH4 systems, investigated previously with the same methodology. Information on the relative orientation of the partners, arising from the anisotropy of the intermolecular interaction, evaluated at different intermolecular distances, has been also obtained. Such information is crucial to evaluate sterodynamics effects in bimolecular collisions.
