Photodissociation dynamics of homonuclear diatomic molecules in helium nanodroplets. The case of Cl2@(4He)N.
Photodissociation dynamics of homonuclear diatomic molecules in helium nanodroplets. The case of Cl2@(4He)N.
A. Vilà, M. González, R. Mayol.
J. Chem. Theory Comput., 11 (2015) 899.
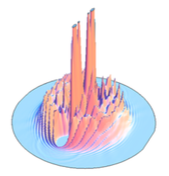
Snapshot showing the helium density (xz plane) close to the final of the [Cl2(B)@(4He)500]* photodissociation process.
A hybrid method based on TDDFT (helium) and quantum dynamics (molecule) was developed to investigate the photodissociation of diatomic homonuclear molecules in superfluid 4He nanodroplets (ND), T=0.37 K, allowing for the first time to study this important type of process. In the first application of this method the Cl2(B←X) photodissociation for Cl2(v=0,X)@(4He)N nanodroplets with N=50-500 was examined. A time scale of a few ps was found for this process and at the high velocities involved an efficient energy exchange between the Cl atoms and the ND occurs, releasing up to 91% of the molecular energy (N=500). Moreover, the strongly oscillating final velocity distribution of the Cl dissociating atoms observed was due to the existence of confinement quantum interferences. As far as we know this is the first time that this type of interferences is described in the reaction dynamics context. We hope that these results will encourage the experimentalists to investigate these interesting systems.
