CO oxidation activity of Pt/CeO2 catalysts below 0°C: platinum loading effects.
A. I. Boronin, E. M. Slavinskaya, A. Figueroba, A. I. Stadnichenko, T. Y. Kardash, O. A. Stonkus, E. A. Fedorova, V. V. Muravev, V. A. Svetlichnyi, A. Bruix, K. M. Neyman.
Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 286 (2021) 119931.
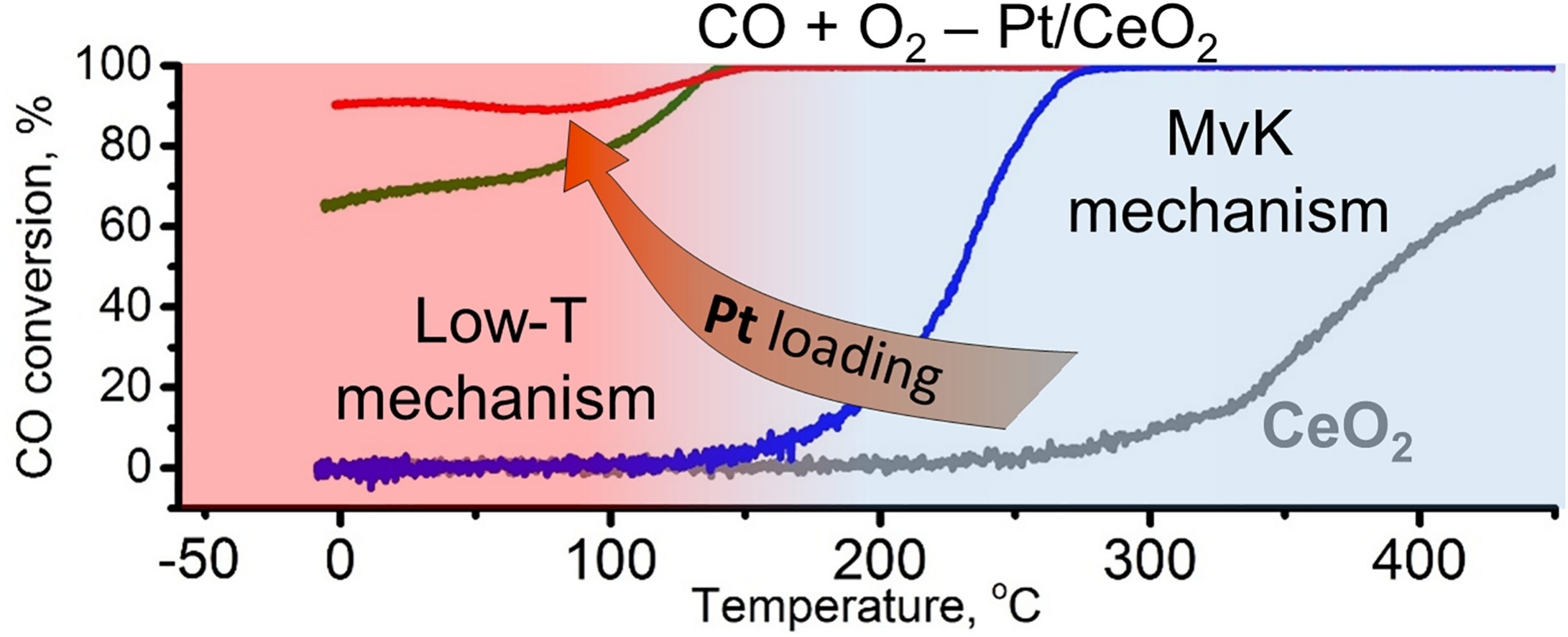
Reducing the operating temperature of oxidation catalysts is important for designing energy efficient processes, extending catalyst lifetime, and abating pollutants, especially in cold climates. Herein, high CO oxidation activity at sub-ambient temperatures is reported for Pt/CeO2 catalysts with high content of Pt in the form of dispersed Pt2+ and Pt4+ centres. Whereas the reference 1 wt% Pt catalyst was active for CO oxidation only above 100°C, the 8 and 20 wt% Pt catalysts converted 60 and 90 % of CO, respectively, below 0°C. Ionic platinum was shown to facilitate oxygen release from ceria and lower the light-off temperature of the reaction occurring through the Mars-van-Krevelen mechanism. However, the remarkable activity observed at subambient temperatures for the ≥8 wt% Pt catalysts is proposed to involve O2 and CO reactants weakly adsorbed on PtOx clusters. The synergies between ionic platinum and nanostructured ceria reported in this work advance the knowledge-driven design of catalysts for low-temperature oxidation reactions.
